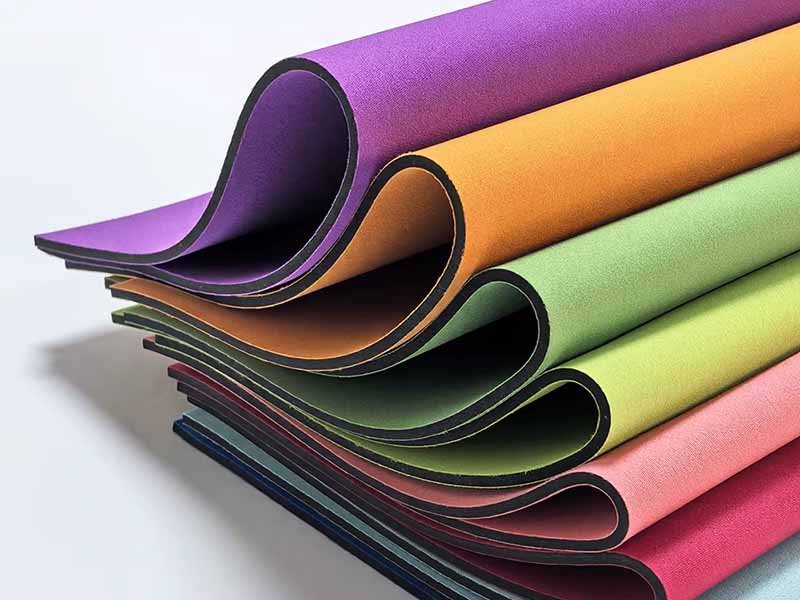
Neoprene has evolved far beyond its original invention in the 1930s as a synthetic substitute for rubber. Today, it’s a versatile material found in everything from wetsuits and laptop sleeves to medical supports and industrial insulation. Its durability, flexibility, water resistance, and insulating properties make it a favorite across multiple industries. For businesses looking to develop neoprene-based products, understanding the different types of neoprene fabric is essential to making cost-effective and performance-driven choices.
The main types of neoprene fabric include open-cell, closed-cell, laminated, coated, and specialty grades designed for industrial, sports, and consumer applications. Each type varies in density, flexibility, thermal insulation, and water resistance—making it essential to match the fabric’s properties to your specific product needs.
Imagine this: A sportswear brand launches a premium wetsuit line but chooses the wrong neoprene type. The suits absorb water, get heavy, and lose flexibility. Customer complaints skyrocket. On the flip side, brands that understand neoprene’s grades and finishes can create high-performing products that win customer loyalty and premium pricing. Let’s explore these types in depth—so your next neoprene-based product is a success from the start.
What Is Neoprene Fabric and How Is It Made?
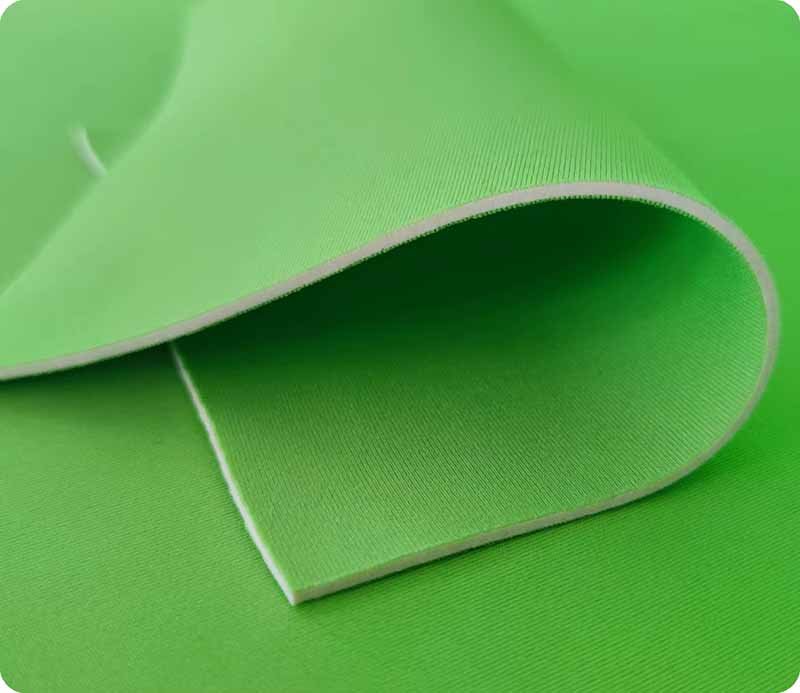
Neoprene fabric is a synthetic rubber material (polychloroprene) created by polymerizing chloroprene. It’s manufactured into foam sheets, then processed into either open-cell or closed-cell structures. Often, it’s laminated with fabrics like nylon or polyester to enhance strength, printability, and comfort.
Neoprene begins its life as liquid chloroprene monomer, which undergoes polymerization to form polychloroprene rubber chips. These chips are melted, mixed with foaming agents, and baked in large molds, creating foam “buns.” Depending on formulation and blowing process, the foam structure becomes either open-cell (more breathable, less water-resistant) or closed-cell (dense, water-resistant, buoyant).
Once cured, the foam is sliced into sheets of varying thickness—from ultra-thin 0.5mm neoprene for fashion and electronics cases to 10mm+ neoprene for heavy-duty wetsuits and industrial insulation. These sheets may remain uncoated or be laminated with fabrics on one or both sides, adding color, printability, and abrasion resistance.
Key Manufacturing Steps:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Polymerization | Chloroprene converted into polychloroprene chips |
| Foaming | Chips blended with blowing agents to create cellular structure |
| Baking & Curing | Heat expansion sets foam density and properties |
| Slicing | Foam buns cut into sheets of required thickness |
| Lamination | Fabric layers bonded for strength and aesthetics |
Which Are the Main Types of Neoprene Fabric by Structure?
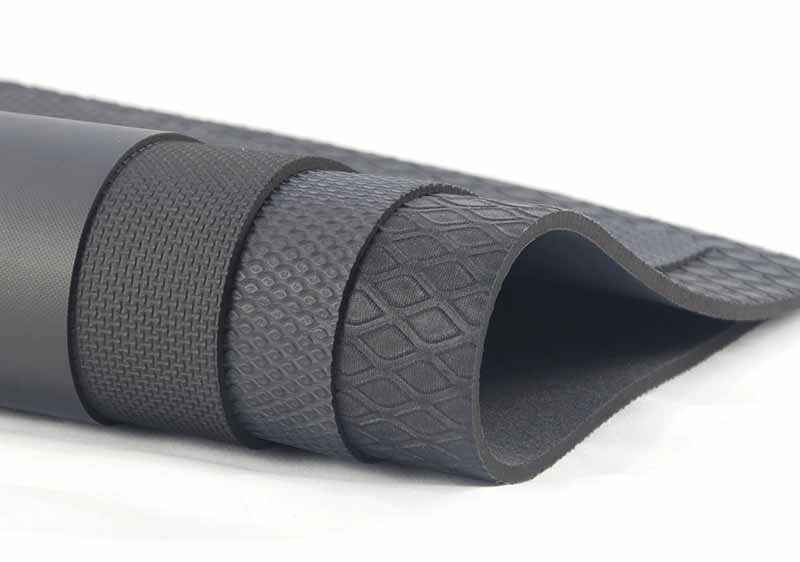

The main structural types of neoprene fabric are open-cell (soft, breathable) and closed-cell (dense, water-resistant). Closed-cell is preferred for wetsuits, bags, and insulation, while open-cell offers superior comfort and flexibility for certain applications.
1. Open-Cell Neoprene
- Sponge-like structure with interconnected air pockets
- Highly flexible and soft
- Excellent for skin contact applications like orthopedic braces
- Poor water resistance—absorbs water easily
2. Closed-Cell Neoprene
- Gas-filled, sealed bubbles
- Excellent buoyancy and water resistance
- More rigid than open-cell
- Ideal for wetsuits, life vests, and protective covers
3. Laminated Neoprene
- Foam laminated with nylon, polyester, or specialty fabrics
- Improves abrasion resistance and color options
- Common in sportswear and consumer goods
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Open-Cell | Closed-Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High | Medium |
| Water Resistance | Low | High |
| Insulation | Medium | High |
| Buoyancy | Low | High |
| Breathability | High | Low |
How Do Neoprene Grades Differ for Industrial and Consumer Use?

The main structural types of neoprene fabric are open-cell and closed-cell. Open-cell neoprene is soft, breathable, and flexible, ideal for comfort-focused applications like braces and padding. Closed-cell neoprene is dense, water-resistant, and buoyant, making it suitable for wetsuits, protective covers, and industrial insulation. Laminated versions combine neoprene with fabrics like nylon or polyester to enhance durability, color options, and printability.
When selecting neoprene for a product, structure matters as much as thickness or grade. The foam’s internal cell structure — whether open, closed, or laminated with fabrics — determines its flexibility, insulation, buoyancy, and water resistance.
CR (Chloroprene Rubber) Neoprene
- 100% pure chloroprene
- Superior chemical, UV, and ozone resistance
- Best for high-performance sports gear and industrial safety equipment
SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) Blends
- Lower cost, moderate performance
- Suitable for general consumer goods
- Less resistant to extreme environments
Specialty Grades:
- Medical-grade neoprene: Hypoallergenic, antimicrobial
- Flame-retardant neoprene: Meets safety codes for protective gear
- Eco-friendly neoprene: Made from recycled or limestone-based chloroprene
Applications by Grade:
Structural Type Comparison Table
| Structure Type | Flexibility | Water Resistance | Insulation | Buoyancy | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open-Cell | High | Low | Medium | Low | Medical braces, padding |
| Closed-Cell | Medium | High | High | High | Wetsuits, flotation gear |
| Laminated | Medium–High | Medium–High | High | Medium–High | Bags, sleeves, apparel |
Why Structure Choice Matters
Choosing the right neoprene structure impacts not only the product’s technical performance but also its market positioning.
- A fitness gear brand might opt for laminated closed-cell neoprene for sweat-resistant waist trimmers that are also durable and printable.
- An industrial buyer could choose pure closed-cell neoprene for marine covers where water resistance is critical.
- A medical equipment supplier may prefer open-cell neoprene for braces that prioritize comfort and skin breathability.
At Szoneier, we help clients match structure type to application, target market, and price point, ensuring that your neoprene products deliver both functional excellence and commercial appeal.
What Types of Neoprene Coatings and Laminations Are Available?
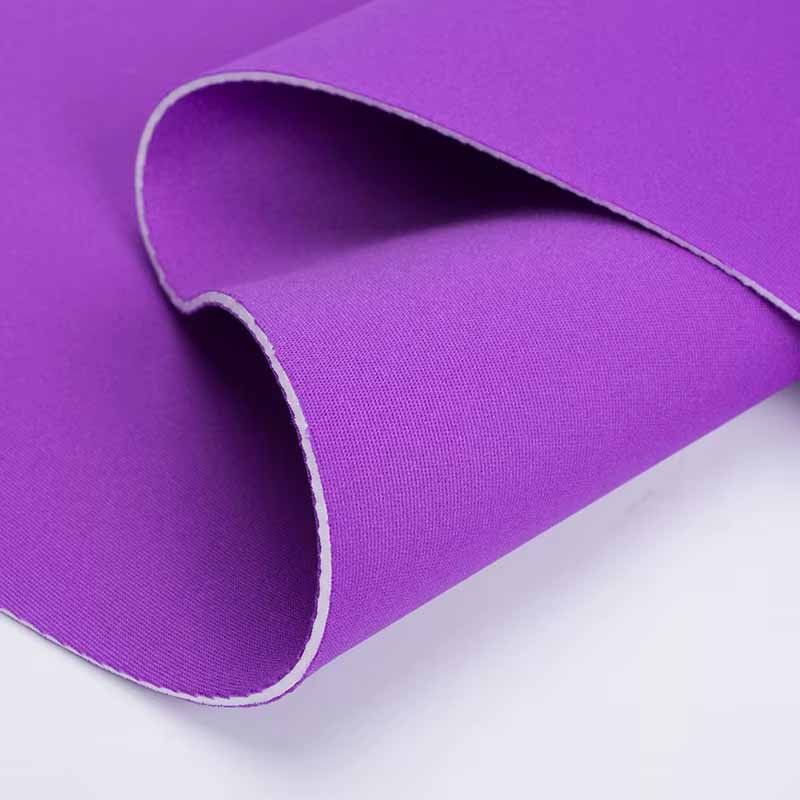

Neoprene can be laminated with nylon, polyester, or specialty fabrics, or coated with smooth skin, mesh skin, or embossed finishes. Laminations improve durability, printability, and comfort, while coatings provide functional benefits like reduced drag, UV resistance, or enhanced grip. Choosing the right combination ensures your neoprene product meets performance, branding, and market positioning goals.
In its raw foam form, neoprene is functional but not always ideal for direct use. Laminations and surface coatings are applied to enhance the fabric’s performance, durability, and aesthetics. For OEM and ODM projects, understanding these finishing options is crucial — they influence both how the end product performs and how it is perceived in the market.
1. Common Neoprene Laminations
Nylon-Laminated Neoprene
- Description: Nylon fabric bonded to one or both sides of the foam.
- Benefits: Excellent abrasion resistance, stretch recovery, and color options.
- Applications: Wetsuits, sports braces, laptop sleeves.
Polyester-Laminated Neoprene
- Description: Polyester fabric bonded to the foam surface.
- Benefits: High print quality and vibrant colors; economical option.
- Applications: Fashion accessories, promotional products, branded merchandise.
Double-Laminated Neoprene
- Description: Fabric laminated on both sides.
- Benefits: Maximizes durability and protects foam from both sides.
- Applications: Sports gear, industrial covers, tool pouches.
Single-Laminated Neoprene
- Description: One side laminated, other side foam for adhesion.
- Benefits: Allows bonding to other materials while keeping one protective fabric surface.
- Applications: Composite panels, hybrid materials, footwear.
2. Neoprene Surface Coatings
Smooth Skin (Glide Skin)
- Benefits: Low drag in water, excellent wind resistance.
- Applications: Triathlon wetsuits, swim caps.
Mesh Skin
- Benefits: UV resistance, abrasion protection, better grip.
- Applications: Surf wetsuits, protective covers, industrial wraps.
Embossed Patterns
- Benefits: Aesthetic branding, improved grip for handling.
- Applications: Fashion neoprene items, grip-enhanced sports gear.
Coating & Lamination Comparison Table
| Finish Type | Key Benefit | Best For | Cost Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon-Laminated | Abrasion resistance, flexibility | Sports gear, sleeves | Medium |
| Polyester-Laminated | Print quality, economy | Promotional goods | Low |
| Double-Laminated | Durability | Heavy-duty use | High |
| Single-Laminated | Hybrid bonding | Footwear, composites | Medium |
| Smooth Skin | Hydrodynamics | Swim gear | High |
| Mesh Skin | UV & abrasion resistance | Outdoor covers | Medium |
| Embossed | Branding, grip | Fashion, sports gear | Variable |
Why This Matters for Your Business
For B2B buyers, the right lamination or coating can mean the difference between a product that meets basic function and one that excels in durability, market appeal, and brand differentiation. For example:
- A sports brand may opt for nylon-laminated, smooth skin neoprene for wetsuits that combine flexibility with low drag.
- An industrial client might prefer double-laminated mesh skin for covers exposed to sun and abrasion.
At Szoneier, we offer full customization in lamination fabrics, coating types, thickness, and colors — so your neoprene products are optimized for performance and market positioning.
Are There Specialized Neoprene Fabrics for Certain Applications?
Yes. Specialized neoprene fabrics are engineered for unique performance needs—such as super-stretch neoprene for wetsuits, fire-resistant neoprene for safety gear, perforated neoprene for breathability, and eco-friendly recycled neoprene for sustainable products. Each variant balances flexibility, durability, and environmental considerations to meet specific industry demands.
While standard neoprene works for many general applications, certain industries require enhanced or highly specific performance features. Manufacturers like Szoneier develop specialized neoprene fabrics to meet these targeted needs without compromising on quality or cost-effectiveness. Here are the most notable types:
1. Super-Stretch Neoprene
- Composition: High-grade CR neoprene with enhanced elongation properties (300–500%)
- Applications: Premium wetsuits, triathlon suits, compression sportswear
- Advantages: Superior comfort, unrestricted movement, tight fit without restricting circulation
- Buyer Insight: Brands selling high-performance sports gear often choose super-stretch neoprene for premium lines, justifying higher retail prices.
2. Fire-Resistant Neoprene
- Composition: Formulated with flame-retardant additives meeting NFPA or EN safety standards
- Applications: Industrial safety apparel, welding blankets, heat shields
- Advantages: Maintains structural integrity under extreme heat, resists ignition
- Buyer Insight: Essential for PPE manufacturers and industrial suppliers needing compliance with fire safety regulations.
3. Perforated Neoprene
- Composition: Closed-cell neoprene with precision-cut perforations for airflow
- Applications: Sports braces, seat covers, breathable fashion accessories
- Advantages: Reduces heat buildup, increases comfort during prolonged wear
- Buyer Insight: Adds a comfort-oriented selling point for consumer products, especially in warm climates.
4. Eco-Friendly Neoprene
- Composition: Made from limestone-based chloroprene or recycled post-consumer neoprene waste
- Applications: Sustainable fashion, eco-conscious sports gear
- Advantages: Lower carbon footprint, appeals to environmentally conscious markets
- Buyer Insight: Strong marketing value for brands with sustainability goals—can improve brand image and market reach.
Specialized Neoprene Comparison Table
| Type | Key Property | Ideal Applications | Performance Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Super-Stretch | 300–500% elongation | Wetsuits, sportswear | Comfort, flexibility |
| Fire-Resistant | Flame retardant | PPE, industrial covers | Heat safety compliance |
| Perforated | Breathable | Braces, covers | Temperature regulation |
| Eco-Friendly | Sustainable material | Eco fashion, sports gear | Environmental marketing edge |
Why It Matters for Your Business
Choosing a specialized neoprene type is not just about meeting functional requirements—it’s about product positioning and long-term customer satisfaction. For example:
- Sportswear brands can differentiate premium lines with super-stretch neoprene.
- Industrial suppliers reduce liability risks with fire-resistant variants.
- Lifestyle brands can tap into sustainability-driven consumers with eco-friendly neoprene.
At Szoneier, we can help you match your application’s performance needs with the right specialized neoprene type—customized in thickness, lamination, and branding to fit your exact product vision.
How to Choose the Right Type of Neoprene Fabric for Your Project?
Choose neoprene based on application needs—thickness, density, stretch, water resistance, and budget. Consult your manufacturer for custom lamination or grade options.
When selecting neoprene, consider:
- Environmental Conditions: Saltwater, chemicals, temperature extremes
- Performance Needs: Flexibility, insulation, buoyancy
- Product Life Expectancy: Long-term durability vs. disposable use
- Aesthetic & Branding: Color, print compatibility
Decision Table:
| Application | Recommended Type | Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| Wetsuits | Super-stretch CR | 3–5mm |
| Laptop Sleeves | SBR blend, laminated | 3–4mm |
| Medical Braces | Open-cell medical grade | 4–6mm |
Do Neoprene Fabrics Require Special Care or Maintenance?
Yes. Neoprene fabrics need proper cleaning, drying, and storage to preserve elasticity, lamination bonds, and overall lifespan. Rinse with fresh water after use, avoid direct sunlight, and store in a cool, dry place. Use mild detergents only, and never expose neoprene to high heat or petroleum-based chemicals to prevent premature aging or damage.
While neoprene is known for its durability, improper care can significantly shorten its service life and affect product performance — especially for items exposed to water, sweat, UV light, or harsh environmental conditions. For businesses supplying neoprene-based goods, understanding and communicating proper maintenance practices to end-users is essential for reducing warranty claims, boosting customer satisfaction, and enhancing brand reputation.
1. Cleaning Best Practices
- Freshwater Rinse: After each use, especially for wetsuits, bags, or sports braces exposed to sweat, saltwater, or chlorine. Salt and chemicals can degrade the foam structure and lamination adhesive over time.
- Mild Detergent: Use a neoprene-specific cleaner or diluted mild soap. Avoid bleach, strong alkaline cleaners, or solvents.
- No Machine Washing: Agitation can weaken lamination layers and stretch seams.
2. Drying Guidelines
- Air-Dry Only: Hang or lay flat in a shaded, ventilated area.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Prolonged UV exposure can cause brittleness, fading, and loss of elasticity.
- No Tumble Dryers or Heaters: High heat can warp foam cells and damage adhesives.
3. Storage Recommendations
- Cool, Dry Place: Prevents mold and mildew growth.
- Avoid Folding for Long Periods: Use wide hangers for garments; roll flat sheets or covers to prevent creasing.
- Keep Away from Oils and Fuels: Petroleum products can chemically degrade neoprene.
4. Maintenance for Longevity
A well-cared-for neoprene product can last 2–3 times longer than one that’s neglected. For example:
- Sportswear brands can reduce returns by providing a “care card” with each product.
- Industrial suppliers can improve the ROI of safety gear by ensuring maintenance protocols are followed on-site.
Care & Maintenance Quick Reference Table
| Care Step | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Rinse in fresh water | Removes salts, sweat, and chemicals |
| Use mild detergent | Prevents chemical damage to foam cells |
| Air-dry in shade | Avoids UV and heat damage |
| Store flat/rolled | Maintains shape and elasticity |
| Keep away from oils | Prevents chemical breakdown |
Conclusion
Whether you need a flexible neoprene for sports gear, a laminated type for bags, or an industrial-grade for safety equipment, the right choice impacts your product’s performance, customer satisfaction, and brand reputation.
At Szoneier, with over 18 years of experience in neoprene R&D and manufacturing, we offer:
- Custom thickness & lamination options
- OEM & ODM production for your branding
- Low MOQ, free design, and rapid sampling
- 100% quality assurance
Contact us today to discuss your custom neoprene project and get a tailored quotation.











